
The study, entitled Metacarpal trabecular bone varies with distinct hand-positions used in hominid locomotion (Christopher Dunmore, Dr Ameline Bardo, Professor Tracy Kivell and Dr Matthew Skinner, Skeletal Biology Research Centre, SAC, University of Kent) was published in the Journal of Anatomy. This matters because when we find ancient human hand fossils that preserve their internal structure, we can work out if they were probably swinging from trees during their lifetime or if they were walking on the ground more like humans today.’ Skeletal maturation in the chimpanzee hand and wrist (the RUS system radius, ulna, and short bones) was studied both longitudinally and cross-sectionally. Mr Dunmore said: ‘For the first time we see interesting internal bone patterns differentiating subtle differences between chimpanzee and gorilla knuckle-walking, as well as arboreal grasping in orang-utans. The information will now enable scientists studying fossils to better understand whether ancient humans were swinging from trees or walking on the ground. The researchers found the knuckle joints of orang-utans were consistent with flexing the knuckles while grasping branches, while the joints of chimpanzees, bonobos and gorillas were consistent with knuckle-walking – the most frequent ways in which these animals move around in their respective environments.

The study compared the internal bone structure of the knuckle joints in chimpanzee, bonobo, orang-utan and gorilla hands, to assess whether this bone structure records how these apes moved when knuckle-walking on the ground or hanging from trees. All to some degree possess prehensile (grasping) hands and all (except humans) prehensile feet. Manipulations requiring precision are usually accomplished with the interaction of the thumb and middle finger, rather than the index finger.
CHIMPANZEE HAND BONE SERIES
The hand of the chimpanzee possesses four long fingers and a shorter opposable thumb. Based on the anatomy of human and chimpanzee hand muscles and the positions of their attachment to individual bones, they have been able to establish a series of parameters that clearly distinguish the morphological and probably functional characteristics of the thumbs of these living primates. When it is preserved in fossils, researchers can learn more about how ancient apes as well as humans moved and interacted with their environment. Almost all primates have five digits on the hand and foot. Articulated rigid hand from Chimpanzee Skeleton SC-003. Trabecular bone is a honeycomb structure that is found within most bones and changes depending on what that bone is used for during a lifetime. Using samples from the Powell-Cotton Museum in Birchington-on-Sea (UK), as well as samples from Germany, Belgium and the USA, a team led by School of Anthropology and Conservation (SAC) PhD student Christopher Dunmore examined the internal bone structure, called trabeculae or cancellous bone, of great apes.
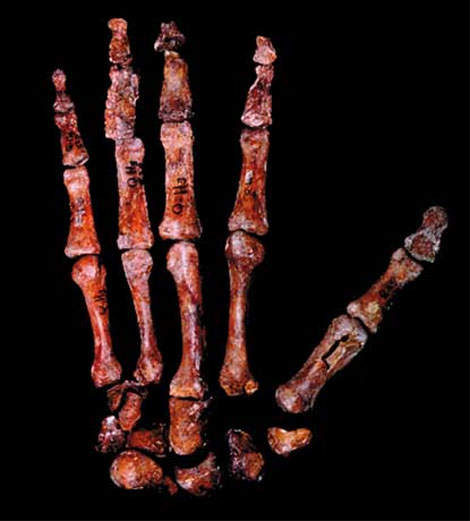
Research carried out by the University has found differences between the knuckle joints of primates that will enable a better understanding of ancient human hand use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
